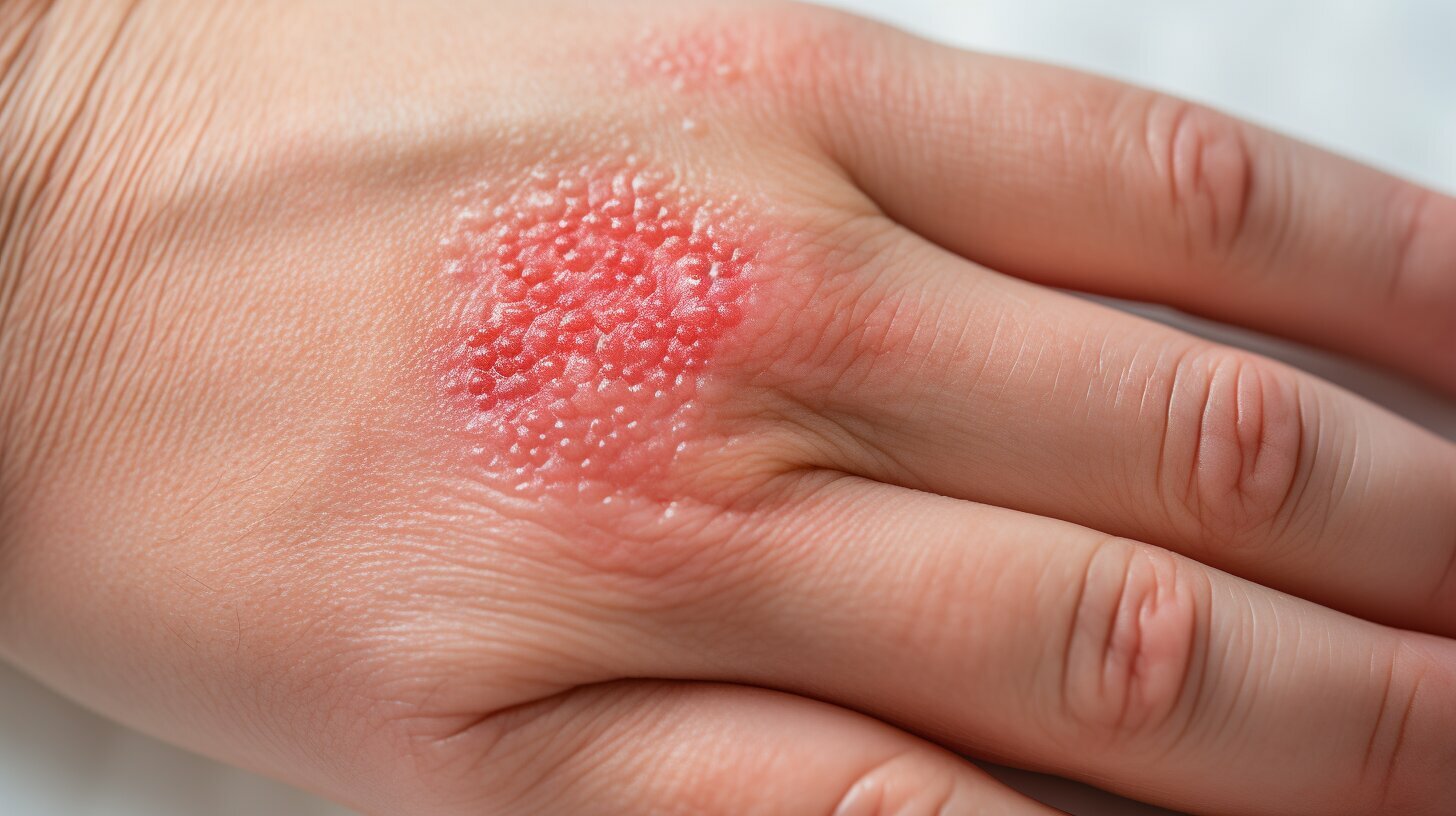
If you’ve ever experienced a painful bump on your skin that resembles a pimple but doesn’t seem to go away, you may have a skin abscess. This common condition can be caused by a bacterial infection and can occur anywhere on the body. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for skin abscesses is important for proper management and prevention of potential complications.
Key Takeaways:
- A skin abscess is a painful, pus-filled bump that can occur anywhere on the body
- It is caused by a bacterial infection that enters the skin through a hair follicle or break in the skin
- Symptoms of a skin abscess include redness, swelling, pain, and warmth around the affected area
- Treatment options may include conservative management techniques, incision and drainage, and antibiotics
- Proper wound care, good hygiene practices, and avoiding skin trauma can help prevent skin abscesses from forming
What is a Skin Abscess?
A skin abscess is a common type of skin infection that occurs when a hair follicle, sweat gland or oil gland becomes infected with bacteria.
An abscess is essentially a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue. It can appear as a red, swollen bump that is painful to the touch. Skin abscesses can occur anywhere on the body, including the face, neck, armpits, groin, and buttocks.
The most common types of bacteria that cause skin abscesses are Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. These bacteria can enter the body through a cut, scratch, or other breaks in the skin, allowing them to infect the surrounding tissue and cause an abscess to form.
Some people are more prone to developing skin abscesses than others. For example, those with weakened immune systems, diabetes, or other chronic conditions may be more susceptible to infection.
Symptoms of Skin Abscess
It’s important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of a skin abscess, so you can identify one if it develops.
The most common symptom of a skin abscess is a swollen, red, and painful lump on the skin. The lump may feel warm to the touch and can range in size from a pea to a golf ball. Other symptoms that may be present with a skin abscess include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Fatigue
- Tenderness around the affected area
- Drainage of pus or fluid from the abscess
- A foul smell coming from the abscess
- Skin redness or inflammation spreading from the abscess
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention right away to receive proper diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of Skin Abscess
A skin abscess is caused by bacteria, usually staphylococcus aureus, entering the body through a break in the skin. The bacteria then begin to multiply, causing an infection that leads to the formation of an abscess.
There are several ways in which bacteria can enter the body and cause a skin abscess. These include:
| Causes of Skin Abscess | Description |
|---|---|
| Ingrown hairs or hair follicles that become infected | When a hair follicle is damaged or blocked, it can become infected and lead to an abscess. This often happens in areas where hair removal occurs frequently, such as the armpits or groin. |
| Cuts, scrapes, or puncture wounds | When the skin is broken, bacteria can easily enter the body and cause an infection. This can happen from a variety of injuries, such as stepping on a nail or getting a paper cut. |
| Boils and other skin conditions | People with pre-existing skin conditions, such as acne or eczema, are more susceptible to developing a skin abscess because their skin is already damaged or prone to infections. |
| Blocked glands or sweat ducts | When sweat ducts or glands become blocked, they can become infected and lead to the formation of an abscess. This often happens in areas where friction or sweating occurs, such as the underarms or groin. |
There are also certain risk factors that can increase your likelihood of developing a skin abscess, including:
- Compromised immune system
- Diabetes
- Poor hygiene
- Living in close quarters with others
- Sharing personal items, such as towels or razors
- Participating in contact sports
Conclusion
Understanding the causes of skin abscesses is an important step in preventing their formation. By practicing good hygiene, taking proper care of wounds and injuries, and avoiding risk factors, you can reduce your likelihood of developing a skin abscess. However, if you do develop a skin abscess, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly to prevent complications and ensure proper treatment.
Diagnosing a Skin Abscess
If you suspect you have a skin abscess, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly. Your healthcare provider will conduct a physical examination and review your medical history to help diagnose the abscess. They may ask about any recent injuries or infections and any medications you are currently taking.
In some cases, your healthcare provider may also order additional tests or procedures to confirm the diagnosis. This may include a blood test, wound culture, or imaging studies, such as an ultrasound or MRI. These tests can help determine the underlying cause and severity of the infection.
Treatment Options for Skin Abscess
There are a variety of treatment options available for skin abscesses, depending on the severity of the infection and the preferences of the patient. Below are some common options that you may discuss with your healthcare provider:
| Treatment Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Warm compresses | Applying warm compresses to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and encourage the abscess to drain on its own. |
| Pain relief | Over-the-counter pain medication such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help manage discomfort associated with the abscess. |
| Incision and drainage | If the abscess does not drain on its own, a healthcare provider may make a small incision and drain the pus from the abscess. This is usually done under local anesthesia. |
| Abscess removal | In some cases, an abscess may need to be surgically removed. This is typically reserved for large or recurrent abscesses. |
| Antibiotics | If the skin abscess is caused by a bacterial infection, your healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics to help clear the infection. |
If your healthcare provider recommends incision and drainage, they will likely provide specific instructions on how to care for the wound after the procedure. This may include keeping the area clean and dry, changing bandages regularly, and avoiding strenuous activity that could irritate the wound.
It is important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions carefully and complete any prescribed course of antibiotics, even if you start feeling better before finishing the entire course. This can help prevent the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and decrease the likelihood of the infection recurring.
Home Remedies for Skin Abscess
While medical treatment is often necessary for skin abscesses, there are also some home remedies that may help alleviate symptoms and promote healing:
- Warm compress: Apply a warm compress to the affected area for 20-30 minutes, three to four times per day. This can help reduce swelling and promote blood flow.
- Tea tree oil: Dilute a few drops of tea tree oil in a carrier oil (such as coconut or almond oil) and apply to the abscess with a cotton ball. Tea tree oil has antibacterial properties that may help fight the infection.
- Garlic: Crush a garlic clove and apply it directly to the abscess. Garlic has natural antibiotic properties that may help fight infection.
- Turmeric: Mix a teaspoon of turmeric powder with water to make a paste and apply it to the abscess. Turmeric has anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce swelling and pain.
- Epsom salt: Dissolve Epsom salt in warm water and soak the affected area for 20-30 minutes, three to four times per day. Epsom salt can help draw out the pus and promote drainage.
While these home remedies may provide some relief, it is important to note that they should never be used as a substitute for medical treatment. Always consult with a healthcare professional if you suspect you have a skin abscess.
Complications of Skin Abscess
If left untreated or poorly managed, a skin abscess can lead to various complications that require medical attention. Some of the potential complications associated with a skin abscess include:
| Complication | Description |
|---|---|
| Cellulitis | A bacterial infection that occurs when the skin and underlying tissues become inflamed and swollen. Cellulitis can spread rapidly and cause serious health complications if left untreated. |
| Sepsis | A potentially life-threatening complication that occurs when bacteria from a skin abscess enters the bloodstream. Symptoms may include fever, chills, low blood pressure, and organ dysfunction. |
| Abscess recurrence | Some people may experience recurrent skin abscesses, particularly those with weakened immune systems or those who have had previous abscesses. Recurrent abscesses may require more aggressive treatment. |
If you notice any of the above symptoms or suspect that your skin abscess is worsening, it is important to seek medical attention promptly.
It is also important to keep the affected area clean and to avoid touching or scratching the abscess, as this can lead to further complications.
Preventing Skin Abscess
Preventing skin abscesses is possible by taking certain precautions in your daily life. Bacteria is the primary cause of skin abscesses, so maintaining good hygiene practices can significantly reduce your risk of infection.
Here are some tips and recommendations for preventing skin abscesses:
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Practice good hand hygiene | Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and warm water before eating, after using the bathroom, and after coming into contact with someone who is sick. |
| Clean and cover wounds | Use soap and water to thoroughly clean any cuts or wounds, and cover them with a clean, dry dressing to prevent bacteria from entering the body. |
| Avoid sharing personal items | Avoid sharing personal items such as towels, razors, or clothing with others to reduce the risk of cross-contamination. |
| Stay healthy | Eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and get enough sleep to maintain a healthy immune system that can fight off infection. |
| Keep your skin clean and dry | Bathing regularly and keeping your skin dry can help prevent bacteria from accumulating and multiplying on the skin’s surface. |
If you have a weakened immune system or underlying medical conditions such as diabetes, you may be at greater risk of developing skin abscesses. It is essential to work closely with your healthcare provider to manage any underlying conditions and reduce your risk of infection.
When to Seek Medical Help
If you have a skin abscess, it is important to seek medical help if the symptoms are severe or if they do not improve with self-care measures. Additionally, you should seek medical attention if:
- The abscess is larger than 1 cm in diameter
- The abscess is located on the face or near the anus or genitals
- You experience fever, chills, or other signs of systemic infection
- You have a weakened immune system
A healthcare professional can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options, such as antibiotics or incision and drainage. Prompt treatment can help prevent complications and ensure a faster recovery.
Skin Abscess in Children
Children are also susceptible to skin abscesses, which can be especially concerning for parents or caregivers. While the causes and symptoms are similar to those in adults, there are some differences to be aware of.
Children who have frequent skin infections, such as impetigo or eczema, may be more prone to developing abscesses. It is important to practice good hygiene with children and teach them to avoid picking at cuts or scrapes to prevent bacterial entry.
If you notice a bump or swelling on your child’s skin, especially if it is warm to the touch and painful, it may be a skin abscess. It is important to seek medical attention for children with suspected abscesses, as the infection may spread and cause more serious complications.
The treatment options for children with skin abscesses are similar to those for adults, but may require special considerations for their smaller size and unique needs. Your healthcare provider will be able to advise on the best course of action for your child’s specific case.
Skin Abscess FAQ
Here are some of the most commonly asked questions about skin abscesses.
Can a skin abscess be contagious?
Yes, a skin abscess can be contagious if the bacteria that caused the abscess are spread to others. It is important to practice good hygiene and avoid contact with the abscess to prevent spreading the infection.
How long does it take for a skin abscess to heal?
The healing time for a skin abscess can vary depending on the size and severity of the infection. With proper treatment, most small abscesses will heal within a few days to a week. Larger, more severe abscesses may take longer to heal.
Can a skin abscess go away on its own?
In some cases, a small abscess may be able to heal on its own without medical treatment. However, it is important to monitor the abscess closely and seek medical attention if the symptoms worsen or persist over time.
How is a skin abscess drained?
A skin abscess can be drained through a small incision made by a healthcare provider. Local anesthesia may be used to numb the area before the procedure. Once the abscess is drained, the healthcare provider may pack the wound with gauze to help it heal properly.
What are the complications of not treating a skin abscess?
If left untreated, a skin abscess can lead to more serious infections, such as cellulitis, or cause the bacteria to spread to other parts of the body. It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have a skin abscess.
Can a skin abscess be prevented?
While it may not always be possible to prevent a skin abscess, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing one. Practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with people who have skin infections, and keeping wounds clean and covered can all help prevent skin abscesses.
Conclusion
Now that you’ve learned about skin abscesses, you understand the importance of prompt treatment and proper management. Remember, skin abscesses can be a serious condition if left untreated, and it’s essential to seek medical attention if you suspect you have one.
If you’re experiencing any symptoms, such as redness, swelling, or pain, it’s vital to take action and get medical help. Your healthcare provider can diagnose your condition and recommend the best course of treatment, which may include antibiotics, drainage, or other therapies.
Finally, taking steps to prevent skin abscesses is also crucial. Good hygiene, wound care, and avoiding risky behaviors can all reduce your risk of developing this condition. By taking care of your skin and seeking prompt medical attention when needed, you can keep yourself healthy and avoid the complications associated with skin abscesses.